การเขียนประโยคภาษาอังกฤษระดับสูงต้องใช้โครงสร้าง Compound-Complex Sentence ให้เป็น หากคุณกำลังมองหาแบบฝึกหัด Compound-Complex Sentence ที่มีเฉลยครบถ้วนและคำอธิบายละเอียด บทความนี้รวบรวมแบบฝึกหัด 30+ ข้อ พร้อมวิธีวิเคราะห์โครงสร้าง สูตรจำง่าย และเทคนิคหลีกเลี่ยงข้อผิดพลาดบ่อย ที่จะช่วยให้คุณเชี่ยวชาญการใช้ประโยคซับซ้อนได้ในเวลาเพียง 1 ชั่วโมง พร้อมนำไปประยุกต์ใช้ในการเขียนจริงได้ทันที
I. ฝึกฝนและทำความเข้าใจ Compound-Complex Sentence ให้เชี่ยวชาญ
1. ทำความรู้จักส่วนประกอบพื้นฐาน
การเข้าใจประโยค Compound-Complex เริ่มต้นจากการรู้จักส่วนประกอบพื้นฐานที่สำคัญ ซึ่งประกอบด้วยประโยคหลักและประโยคย่อยที่มารวมกันอย่างสมบูรณ์
- Independent Clause (ประโยคหลัก) คือประโยคที่สามารถยืนหยัดอยู่ได้เองโดยไม่ต้องพึ่งพาส่วนอื่น เปรียบเหมือนคนที่พออยู่ตัวคนเดียวได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น “She finished her homework” (เธอทำการบ้านเสร็จแล้ว) เป็นประโยคที่สมบูรณ์ มีทั้งประธานและกริยา
- Dependent Clause (ประโยคย่อย) คือประโยคที่ต้องพึ่งพาประโยคหลักจึงจะให้ความหมายที่สมบูรณ์ เหมือนคนที่ต้องอาศัยผู้อื่น ตัวอย่างเช่น “because she wanted to watch TV” (เพราะเธออยากดูทีวี) ถึงแม้จะมีประธานและกริยาแต่ไม่สามารถยืนอยู่ตัวเองได้
คำเชื่อมสำคัญที่ต้องรู้
คำเชื่อมแบ่งออกเป็นสองประเภทหลักที่คุณต้องเข้าใจ
Coordinating Conjunctions (คำเชื่อมเชิงประสาน)
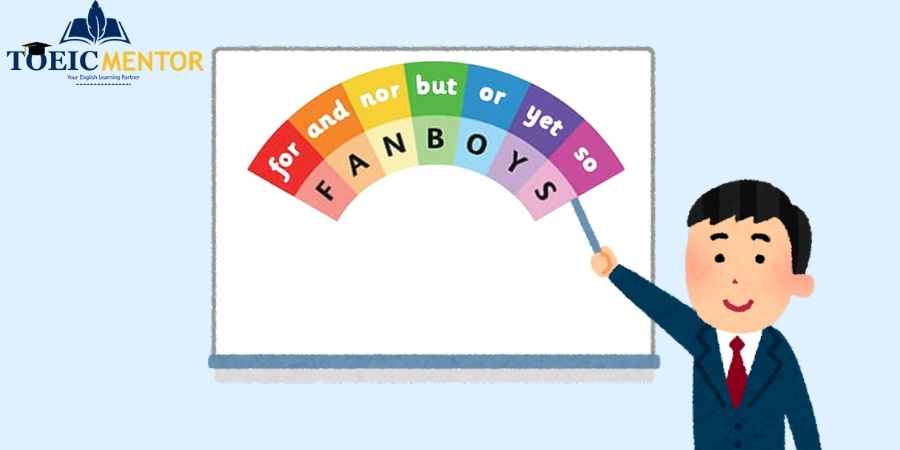
| ตัวอักษร | คำเชื่อม | ความหมาย |
| F | for | เพราะ/สำหรับ |
| A | and | และ |
| N | nor | ไม่…เช่นกัน |
| B | but | แต่ |
| O | or | หรือ |
| Y | yet | แต่/อย่างไรก็ตาม |
| S | so | ดังนั้น |
Subordinating Conjunctions (คำเชื่อมเชิงผูกพัน) ที่ใช้บ่อยที่สุด ได้แก่ because (เพราะ), while (ขณะที่), if (ถ้า), although (แม้ว่า), when (เมื่อ), since (เนื่องจาก), และ unless (เว้นแต่)
2. โครงสร้างและสูตรที่ต้องจำ
สูตรเหล็กของ Compound-Complex Sentence
สูตรพื้นฐานที่คุณต้องจำให้ขึ้นใจคือ: IC (อย่างน้อย 2) + DC (อย่างน้อย 1)
ประโยค Compound-Complex จะต้องมีประโยคหลักอย่างน้อยสองประโยค และประโยคย่อยอย่างน้อยหนึ่งประโยค การจัดเรียงสามารถทำได้หลายรูปแบบตามความต้องการของเนื้อหา
ตัวอย่างการวิเคราะห์โครงสร้าง
มาดูตัวอย่างประโยคจริงเพื่อเข้าใจโครงสร้างให้ชัดเจน:
“Although it was raining (DC), Sarah went to the market (IC), and she bought fresh vegetables (IC).”
การวิเคราะห์:
- [Although it was raining] = Dependent Clause (ประโยคย่อย)
- [Sarah went to the market] = Independent Clause ที่ 1 (ประโยคหลักที่ 1)
- [she bought fresh vegetables] = Independent Clause ที่ 2 (ประโยคหลักที่ 2)
ตัวอย่างนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าประโยคหนึ่งสามารถมีความซับซ้อนแต่ยังคงโครงสร้างที่ชัดเจน
II. แบบฝึกหัด Compound-Complex Sentence พร้อม เฉลย
1. แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1: การจำแนกประเภทประโยค
- When the bell rang, students rushed to the cafeteria, and they formed long lines.
- She studied hard for the exam, but she forgot her calculator at home.
- Because he was tired, Tom went to bed early, and his roommate continued studying.
- The movie was exciting, yet some people left before it ended.
- If you finish your work, you can go home, or you can stay for overtime.
- Although the weather was cold, we decided to go hiking, and we enjoyed the fresh air.
- She wanted to buy a new dress, so she saved money for three months.
- While I was cooking dinner, my brother cleaned the house, and my sister did her homework.
- The concert was cancelled, but the fans waited outside the venue.
- Since it was getting late, we hurried to the station, and we caught the last train.
2. แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2: การรวมประโยคให้เป็น Compound-Complex
รวมประโยคต่อไปนี้ให้เป็น Compound-Complex Sentence:
- It was snowing heavily. The roads were dangerous. We decided to stay home.
- Sarah loves reading books. She goes to the library every weekend. She borrows five books each time.
- The restaurant was crowded. We had to wait for thirty minutes. The food was worth the wait.
- Mark studies computer science. He wants to become a programmer. His parents support his decision.
- The flowers were beautiful. The garden smelled wonderful. Many visitors took photographs.
3. แบบฝึกหัดที่ 3: การเติมคำเชื่อมที่เหมาะสม
เติมคำเชื่อมที่เหมาะสมในช่องว่าง:
- _______ the traffic was heavy, we left early, _______ we arrived on time.
- She practiced piano every day, _______ _______ she was tired, she never missed a lesson.
- The team worked hard, _______ they didn’t win the championship _______ their effort was appreciated.
- _______ you call me tonight, I’ll be waiting, _______ you can send a message instead.
- The book was interesting, _______ some chapters were difficult _______ I needed to read them twice.
4. เฉลยและคำอธิบายละเอียด
- เฉลยแบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
- Compound-Complex – มี DC: “When the bell rang” และ IC สองประโยค: “students rushed to the cafeteria” และ “they formed long lines”
- Compound – มีเพียง IC สองประโยคเชื่อมด้วย “but” ไม่มี DC
- Compound-Complex – มี DC: “Because he was tired” และ IC สองประโยค เชื่อมด้วย “and”
- Compound – มี IC สองประโยคเชื่อมด้วย “yet” แต่ไม่มี DC
- Compound-Complex – มี DC: “If you finish your work” และ IC สองประโยค เชื่อมด้วย “or”
- Compound-Complex – มี DC: “Although the weather was cold” และ IC สองประโยค
- Compound – มี IC สองประโยคเชื่อมด้วย “so” ไม่มี DC
- Compound-Complex – มี DC: “While I was cooking dinner” และ IC สองประโยค
- Compound – มี IC สองประโยคเชื่อมด้วย “but” ไม่มี DC
- Compound-Complex – มี DC: “Since it was getting late” และ IC สองประโยค
- เฉลยแบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
- “Because it was snowing heavily and the roads were dangerous, we decided to stay home.” หรือ “It was snowing heavily, so the roads were dangerous, and we decided to stay home.”
- “Since Sarah loves reading books, she goes to the library every weekend, and she borrows five books each time.”
- “Although the restaurant was crowded and we had to wait for thirty minutes, the food was worth the wait.”
- “Because Mark studies computer science and wants to become a programmer, his parents support his decision.”
- “When the flowers were beautiful and the garden smelled wonderful, many visitors took photographs.”
- เฉลยแบบฝึกหัดที่ 3
- “Although / and” – ใช้ “Although” เพื่อแสดงความขัดแย้ง และ “and” เพื่อเชื่อมผลลัพธ์
- “and / even though” – ใช้ “and” เชื่อม IC และ “even though” แสดงความขัดแย้ง
- “but / although” – ใช้ “but” แสดงความขัดแย้งและ “although” เพื่อยอมรับข้อเท็จจริง
- “If / or” – ใช้ “If” สำหรับเงื่อนไขและ “or” เพื่อแสดงทางเลือก
- “but / so” – ใช้ “but” แสดงความขัดแย้งและ “so” แสดงผลลัพธ์
บทความแนะนำอ่านต่อ:
III. เทคนิคและข้อควรระวัง
1. การใช้ Comma อย่างถูกต้อง
กฎสำคัญในการใช้ comma คือต้องใส่หน้า Coordinating Conjunctions เมื่อเชื่อม Independent Clauses และใส่หลัง Dependent Clause ที่อยู่ต้นประโยค เช่น “Although he was tired, he continued working, but he made several mistakes.”
2. การเลือกใช้คำเชื่อมที่เหมาะสม
คำเชื่อมที่มีความหมายใกล้เคียงกันสามารถใช้แทนกันได้ เช่น “because” และ “since” ต่างก็แสดงเหตุผล แต่ “since” มักใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ผู้ฟังรู้อยู่แล้ว ส่วน “because” ใช้เมื่อต้องการเน้นเหตุผลอย่างชัดเจน
3. ประโยชน์ในการเขียนเชิงวิชาการ
การใช้ Compound-Complex Sentence ช่วยให้งานเขียนดูเป็นระบบและแสดงความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างแนวคิดต่างๆ ได้อย่างชัดเจน นักเขียนที่เชี่ยวชาญมักใช้โครงสร้างนี้เพื่อสร้างความน่าเชื่อถือและความลึกซึ้งในเนื้อหา
IV. คำถามที่พบบ่อยและข้อสงสัยเชิงลึก
1. ประโยค Compound-Complex ต้องยาวเสมอหรือไม่?
ไม่จำเป็นต้องยาวเสมอ ความซับซ้อนของโครงสร้างไม่ได้วัดจากความยาว แต่วัดจากจำนวนและการจัดเรียงของ Independent และ Dependent Clauses ประโยคสั้นก็สามารถเป็น Compound-Complex ได้ถ้ามีโครงสร้างครบถ้วน
2. ข้อผิดพลาดที่พบบ่อยที่สุดคืออะไร?
ข้อผิดพลาดที่พบบ่อยคือการเชื่อม Independent Clause ด้วย comma เพียงอย่างเดียวโดยไม่มี conjunction ซึ่งเรียกว่า “comma splice” ตัวอย่างผิด: “It was raining, we stayed inside.” ควรแก้เป็น “It was raining, so we stayed inside.” หรือ “Because it was raining, we stayed inside.”
3. คำเชื่อมแต่ละประเภทใช้เมื่อไร?
| ประเภท | คำเชื่อม | การใช้งาน |
| เวลา | when, while, after, before | บอกลำดับเหตุการณ์ |
| เหตุผล | because, since, as | อธิบายสาเหตุ |
| เงื่อนไข | if, unless, provided | แสดงเงื่อนไขหรือสมมติฐาน |
| ความขัดแย้ง | although, though, even though | แสดงความแตกต่างหรือข้อยกเว้น |
4. ความแตกต่างระหว่าง Compound และ Compound-Complex
ความแตกต่างหลักคือ Compound Sentence มีเพียง Independent Clauses เท่านั้น ในขณะที่ Compound-Complex จะต้องมี Dependent Clause ด้วย
Compound: “She studied hard, and she passed the exam.” (IC + IC) Compound-Complex: “Because she studied hard, she passed the exam, and her parents were proud.” (DC + IC + IC)
การฝึกฝนแบบฝึกหัด Compound-Complex Sentence เป็นเพียงจุดเริ่มต้นในการพัฒนาทักษะการเขียนภาษาอังกฤษ เมื่อคุณเข้าใจโครงสร้างและสามารถจำแนกประเภทประโยคได้อย่างถูกต้องแล้ว ขั้นตอนต่อไปคือการนำความรู้นี้ไปใช้ในการเขียนเรียงความ รายงาน หรือการสื่อสารในชีวิตประจำวัน การเขียนประโยคที่มีโครงสร้างหลากหลายจะช่วยให้งานเขียนของคุณน่าสนใจ มีความลึกซึ้ง และสื่อความหมายได้อย่างชัดเจนมากยิ่งขึ้น

